FAQ
- Home
- FAQ
Roofing Help & FAQ
If you need help and have questions about some of the roofing terms. This page will help you understand more about roofing and roofers.
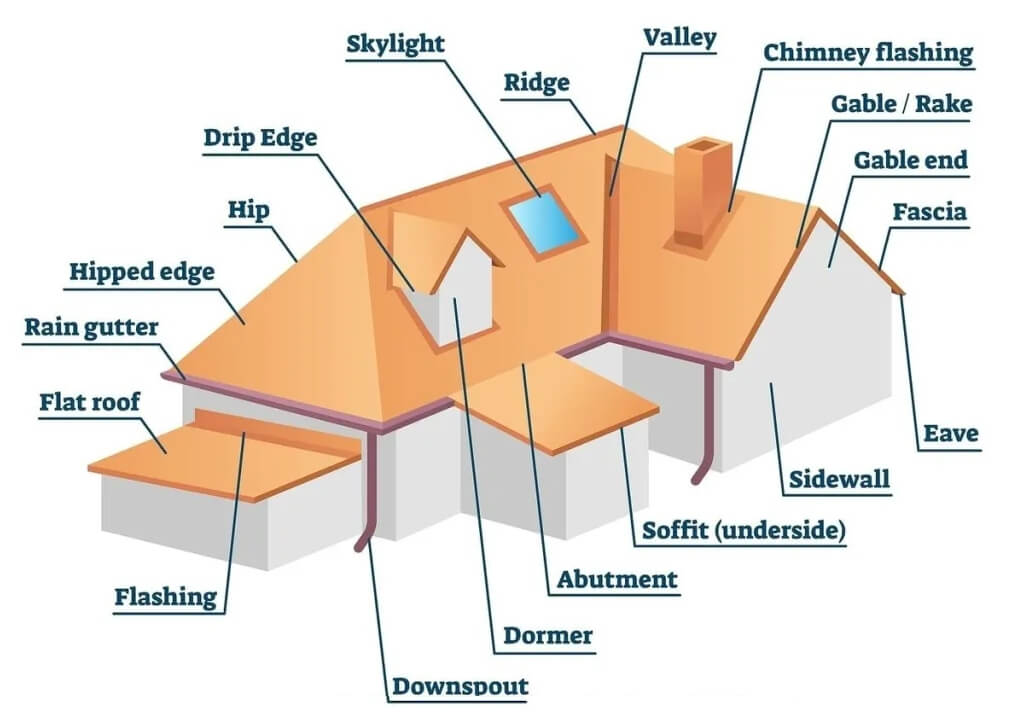
Roof flashing is a technique used to prevent water from penetrating a roof where it intersects with other surfaces, such as a chimney, skylight, pipe vents, or dormer. Flashing is typically made of metal, such as aluminum or copper, and is installed to direct water away from vulnerable areas.
1. The Roof Deck: The roofing deck is the layer of the roof, usually made of plywood or wood and is the foundation for the rest of the roof.
2. Underlayment: The underlayment is a layer of material placed on top of the roof deck and under the shingles or other roofing materials. It acts as a barrier against moisture, provides additional insulation, and helps to protect the roof from damage.
3. Roofing Material: The roofing material is the outermost layer of the roof and serves as the primary barrier against the elements. It can be made of various materials, such as shingles, tiles, metal, or slate, and is chosen based on factors such as durability, cost, and aesthetic appeal.
4. Flashing: Flashing is the thin strip of metal that is formed around roof penetrations, such as chimneys, pipe vents, turtle vents and skylights, to prevent water from leaking in around these areas. It helps to create a watertight seal and protect the roof from leaks.
A roof drip edge, also known as an eave drip or gutter apron, is a narrow peice of metal that is installed along the edges of a roof. It's generally made of steel or aluminum and is installed under the roofing material, extending over the eaves and into the gutters.
The primary function of a roof drip edge is to prevent water from getting into the fascia board, roof deck, or insulation below the roof edge. It helps to direct water away from the roof and into the gutters, preventing water damage to the roof and the home's structure.
Yes, it is possible to repair just a section of a roof. If the damage is in a particular area of the roof, it may not be necessary to replace the entire roof. Roof repairs can be done to fix leaks, damage caused by weather or falling objects or to replace shingles that are missing or damaged. There might also be issues matching the current shingles you have if they were discontinued.
It really depends on the size of the house and the pitch of the roof. It generally takes 24 to 48 to complete a roof install on an average size house.
Decking on a roof refers to a wooden or composite platform on top of a roof structure that the shingles are nailed to. Decking on a roof is typically built with pressure-treated lumber 4x8 or durable composite materials to withstand the elements and provide long-lasting performance.
When roofers refer to "squares," they are talking about a unit of measurement used in the roofing industry to quantify the amount of shingles needed for a job. One square equals 100 square feet (or a 10x10 foot area) of roof surface. This unit of measurement is commonly used for roofing shingles and other types of roofing materials.
For example, if a roofer is working on a roof that is 2,000 square feet in area, they would need 20 "squares" of shingles to cover the entire roof.
A valley on a roof is an area where two roof planes come together at an angle, creating a V-shaped or U-shaped channel. Valleys are typically formed when two roof slopes intersect, such as on a gable or hip roof. They are an important part of the roofing system, as they help to channel water and debris off the roof and into the gutters.
On a roof, the hip is the inclined angle formed by the intersection of the two sloping sides of a roof. Hips are typically found on roofs with four or more sides, such as hip or mansard roofs. They can be either simple or compound, depending on the complexity of the roof design. The hip serves an important function in the roofing system by providing structural support and stability to the roof. It helps evenly distribute the weight of the roof evenly and prevents the roof from collapsing under heavy snow or wind loads. Hips also play a role in directing water and debris off the roof and into the gutters, helping to prevent water damage and other issues.
The gable is a triangular-shaped portion of a wall that is enclosed by the sloping edges of a roof. It is typically located at the end of a pitched roof, where the two roof planes meet to form a ridge.
Gables serve a critical function in the roofing system by providing structural support to the roof and helping to direct water and debris away from the roof and into the gutters. They also play a role in the home's aesthetic appearance, as they can be customized with various types of roofing materials and finishes to complement the style and design of the house.
Fascia on a roof is a vertical band or board that runs along the edge of the roofline, connecting the roof to the house's outer walls. It is typically a long, straight board installed horizontally just below the roof's edge.
The fascia serves several vital functions in the roofing system. It provides a smooth, even surface for attaching the gutters to the roof, helping to direct water and debris away from the roof and prevent damage from moisture. It also helps to support the lower edge of the roof tiles or shingles and provides a finished look to the roofline.
A dormer is a structural element of a house that protrudes from the roof, typically containing a window or windows. It is a roofed structure that is added onto an existing roof, creating additional headroom or usable space within the attic or top floor of the house.
Dormers are often added to houses with steeply-pitched roofs to provide more natural light and ventilation to the upper levels of the house. They can also be used to create additional living space, such as a bedroom, office, or bathroom, by expanding the usable area of the top floor.
The eave is the part of the roof that overhangs beyond the walls of a house. The roof's horizontal edge extends beyond the exterior walls, providing protection from the elements and directing rainwater away from the walls and foundation of the house.
The eave is an essential part of the roofing system, as it helps prevent water damage and rot to the house's roof and walls. It also provides shade to the windows and walls of the house, helping to keep the interior cool and comfortable during hot weather.
A roof vent is a ventilation system installed on the roof of a house or building to allow air circulation and release moisture and heat. Roof vents are a critical component of the roofing system, as they help prevent moisture buildup and condensation in the attic or roof space, which can damage the roof and other parts of the building.
Roof vents come in a variety of different styles and shapes, including ridge vents, turbine vents, box vents, and static vents. Ridge vents run along the length of the roof peak and are often concealed from view, while turbine vents have rotating vanes that spin with the wind to draw hot air out of the attic. Box vents are square or rectangular vents installed on the roof and static vents
The term, rakes refer to the sloped edges of a roof that extend from the eaves to the ridge. Rakes can be found on both gable and hip roofs, and they play a crucial role in protecting the roof from wind-driven rain and other weather elements. Rake overhangs can vary in size, depending on the design of the roof, and they can be trimmed with various materials, such as metal, wood, or vinyl. Proper installation and maintenance of rake edges are essential to ensure the longevity and integrity of a roof.
The terminology for roof overhang is the rake. The rake is the sloped edge of a roof at the end of the ridge or the eave. It overhangs the wall and extends beyond the side of the building, providing protection for the walls and foundation. Rake edges can be vulnerable to weather elements, which is why proper maintenance and installation are important for the longevity and effectiveness of a roofing system.
Blind Nailing is a method of attaching shingles to a roof without any exposed nails or fasteners. In this method, nails are driven through the top edge of the shingle and then covered by the next layer of overlapping shingles. This creates a clean, streamlined look and helps prevent wind damage by securing the shingles more firmly to the roof. Blind Nailing is a preferred method of installation for many roofing contractors and is an important factor in ensuring the longevity and durability of a roof.
Shingles are typically made of asphalt and fiberglass, although some can be made from wood, slate, metal, or other materials. Asphalt shingles are the most commonly used type of shingle due to their durability, affordability, and ease of installation. The asphalt is typically mixed with small granules of ceramic or rock to create a rough texture for better traction and to protect against UV rays. The fiberglass layer provides strength and stability to the shingle, allowing it to withstand wind, rain, and other weather conditions.
